The Role of Pharmaceutical Regulation
In July 2020, the Trump administration officially began the process of withdrawing the United States from the World Health Organization (WHO), citing concerns over the organization's handling of the COVID-19 pandemic and alleged bias toward certain member states.
The U.S. Withdrawal from the WHO: A Turning Point, Not an End to Pharmaceutical Regulation
This decision sent shockwaves across the global health sector, raising fears about the potential erosion of international cooperation and the implications for public health in the U.S. and beyond. After being reversed by the Biden administration in 2021, an Executive Order in January 2025 confirmed the withdrawal.
This has brought to light an important conversation: even outside global institutions like the WHO, health sector regulation remains essential.
For industries such as pharmaceuticals, where precision and safety are paramount, regulatory oversight does not and cannot simply disappear. One key example of why stringent monitoring and pharmaceutical regulation are necessary lies in the handling of temperature sensitive pharmaceuticals.
The Critical Role of Pharmaceutical Temperature Monitoring
Many pharmaceutical products, including vaccines, insulin, weight loss drugs and biologics, are highly sensitive to elevated temperatures (and sometimes low temperatures). Improper storage or transport can render life saving drugs ineffective or even dangerous.
To ensure safety and efficacy, pharmaceutical companies adhere to strict guidelines for manufacturing, storing, and transporting these products. These guidelines, often mandated by regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and other national authorities, underscore the importance of oversight.
For instance, vaccines typically require storage in a cold chain environment, maintaining temperatures between 2°C and 8°C. A break in the cold chain—whether during transportation or storage—or unusual seasonal weather patterns, can compromise the vaccine's potency.
Even in developed nations, logistical mishaps occasionally lead to vaccine spoilage, illustrating the need for continuous monitoring and robust regulatory frameworks.
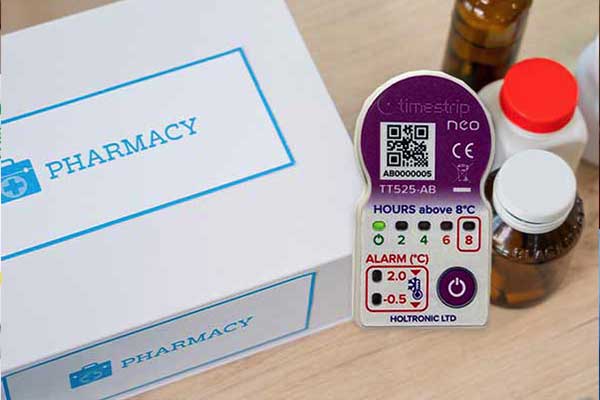
Timestrip temperature and time indicators are designed to accompany sensitive products and to provide clear, irreversible alerts should breaches in expected conditions occur. A large range of indicators, both liquid-based and electronic, is available for standard temperature ranges, and custom specifications can be supplied.
Real-World Examples of Regulatory Impact
One prominent case highlighting the importance of regulation involved the global distribution of COVID-19 vaccines. The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, which requires ultra-cold storage at -70°C, posed significant logistical challenges.
Pharmaceutical companies, governments, and third-party logistics providers collaborated to develop specialized freezers, insulated containers, and temperature-monitoring devices to meet these demands. Regulatory agencies played a crucial role by setting standards, inspecting facilities, and certifying transportation methods to ensure compliance.
Timestrip introduced a range of specialised indicators, capable of monitoring vaccine temperature from the manufacturer (deep freeze), via logistics to primary healthcare centres (fridge), and then to the patient (room temperature).
Another example is the handling of insulin, a life-saving drug for millions of people with diabetes. Insulin must be stored typically between 2°C-8°C controlled temperatures to maintain its effectiveness. Inconsistent storage can lead to degraded insulin, potentially putting patients' lives at risk.
Timestrip temperature indicators provide peace of mind for healthcare professionals that every vial of insulin, from the factory floor to the pharmacy shelf, has not been compromised by adverse environmental conditions.
The Necessity of Continued Oversight
While the US withdrawal from the WHO raised concerns about international collaboration, it by no means signalled the end of regulation in the health sector. National and regional regulatory agencies, as well as private sector stakeholders, remain committed to safeguarding public health.
Advances in technology, such as Timestrip’s purpose designed range of Timestrip neo electronic temperature indicators, have bolstered the ability to track and maintain proper conditions for sensitive pharmaceuticals.
Smart sensors such as these now allow for continuous temperature tracking during the transportation of pharmaceuticals. These devices provide alerts if temperatures deviate from the acceptable range, enabling immediate corrective action.
Some Timestrip indicators provide a ‘mini-data logger’ function and allow users to download a file of time and temperature data to any Internet-connected device. Such innovations underscore the importance of maintaining rigorous standards and enforcing compliance.
Future of Pharmaceutical Regulation
Whether it involves monitoring the temperature of vaccines or ensuring the integrity of cancer drugs, stringent oversight remains non-negotiable. These measures protect not only individual patients but also the broader public, preventing outbreaks, safeguarding supply chains, and maintaining trust in the healthcare system.
The challenges posed by sensitive products such as temperature sensitive medications underscore the ongoing need for rigorous oversight. By leveraging technological innovations and adhering to established standards, the healthcare industry can continue to ensure the safety and efficacy of its therapeutic products.